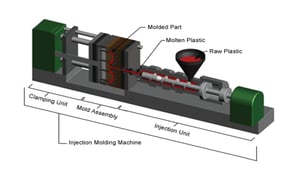
Plastic injection molding is the manufacturing process for fabricating plastics parts of varying sizes, complexity, and application. The process requires a vertical or horizontal injection molding press, a mold, and raw plastic resin. The plastic resin material is melted in the injection molding machine and then injected into the mold, where it cools and solidifies into the final part or parts. The process consists of four stages that include Clamping, Injection, Cooling, and Ejection.
Clamping Unit of Injection Molding Machine
1. Clamping consists of each half of the injection mold is attached to the injection molding machine via the clamping unit. The powered clamping unit pushes the mold halves close and exerts sufficient force to keep the mold securely closed while the liquid resin material gets injected into the mold cavities.
 The time required to clamp the mold and hold it closed depends on the size of the molding press. Clamping is one factor you will need to determine the size of the injection molding press required to manufacture your component. Once you know the size press your part requires, you'll know one element your injection molder needs to produce your product.
The time required to clamp the mold and hold it closed depends on the size of the molding press. Clamping is one factor you will need to determine the size of the injection molding press required to manufacture your component. Once you know the size press your part requires, you'll know one element your injection molder needs to produce your product.
Injection Phase of Resin Raw Material
2. Injection is when the raw material is fed into the injection molding press and advanced toward the mold by the injection unit. During the advancement, raw resin material becomes melted by heat and pressure. The injection unit takes the molten plastic using the build-up of pressure packs and hold the material in the cavities of the mold.
For accurate melt temperatures, a combination of settings needs to be applied, including the barrel temperature, nozzle temperature, and injection mold. The barrel and nozzle temperatures impact the flowability of the plastics throughout the mold. The mold temperature affects the flow through the mold as well as the cooling down of the molded part. The barrel and nozzle temperatures set should be considered carefully. If the temperatures are set too high, it produces an overflow and flash, and too low of a temperature can result in unfilled parts.
Plastic pressure is another element of injection molding. It refers to the physical force applied to the melted resin by the head of the screw when the screw moves forward, a process controlled by the automated system of the injection molding press.Temperature and pressure are two of the elements adjusted when establishing a stable injection molding process.
Cooling Time for Plastic Injection Molding
3. Cooling of the molten plastic inside the mold cavities will solidify into the shape of the part. Cooling begins inside the mold as soon as it makes contact with the interior mold surfaces. The mold will not open until the required cooling time has elapsed. The resin raw material manufacturer provides recommendations for establishing the injection mold temperature. The part and mold designs, as well as the resin raw material used, helps determine the cooling times. The injection mold design incorporates internal cooling.
Ejection of Plastic Part
4. Ejection occurs after the required time has passed to cool the part. When the clamping unit opens the injection mold, an ejection mechanism pushes the part/parts out of the mold. During the cooling process, the component shrinks and adheres to the mold cavities requiring force to eject the part. After the ejection and removal of the part or parts, the mold closes for the injection of the next shot, starting the next cycle.
Now that you have a high level overview of the plastic injection molding process, review the Complete Guide for Plastic Injection Molding and learn more about the different types of injection molding, equipment used, injection molding process monitoring for quality components and more.


